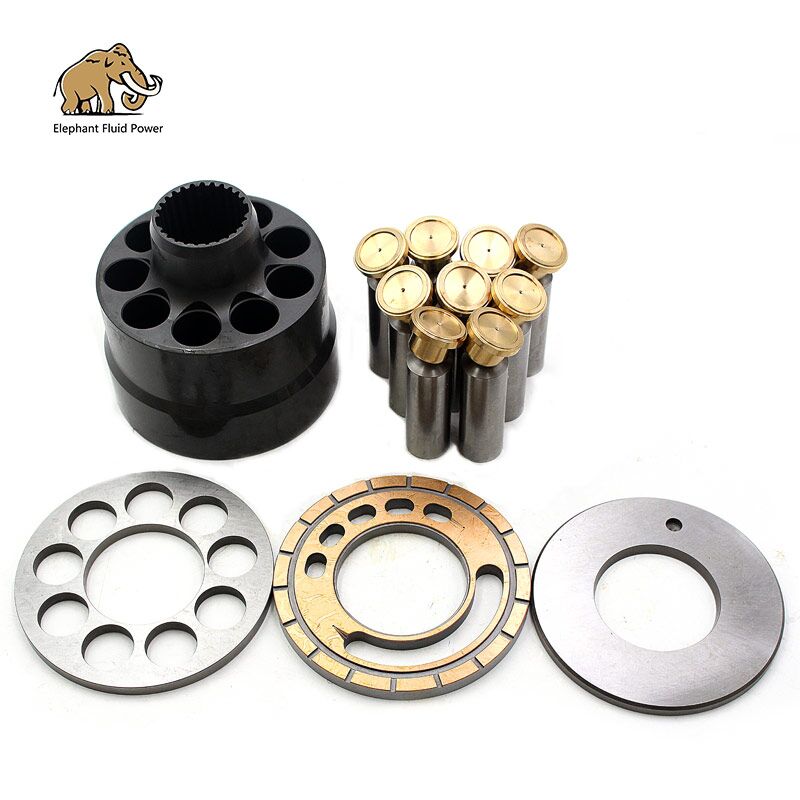
The K3V hydraulic pump is an axial piston pump commonly used in construction machinery and other fields. Below are its general maintenance steps:
First, Preliminary Preparation
1. Safety precautions: Before maintenance, ensure the equipment is shut down, disconnect the power source or drive source, and relieve pressure in the hydraulic system to prevent accidents during repairs. For example, in systems with accumulators, pressure must first be released from the accumulator using the correct method.
2. Tool and Material Preparation: Gather necessary repair tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, calipers, dial indicators, and appropriate materials like seals and hydraulic fluid.
3. Site Cleanup: Clear the work area and maintain a clean environment to prevent debris from entering the pump.
Second, Fault Diagnosis
1. Observation and Inquiry: Consult the equipment operator about conditions before and after the failure, such as unusual noises, vibrations, or pressure changes. Simultaneously, visually inspect the pump for obvious issues like leaks or damage.
2. Pressure and Flow Testing: Use specialized pressure and flow testing equipment to verify the pump's output pressure and flow rate. Insufficient pressure or unstable flow may indicate internal component wear, damage, or blockages.
3. Noise and Vibration Analysis: Operate the pump while listening for abnormal noises and feeling for unusual vibrations. Noise may stem from component wear, cavitation, or hydraulic shock; vibration could relate to unstable pump mounting or component imbalance.
Third, Disassemble the Pump Housing
1. Marking and Documentation: Before disassembly, mark and document the position and orientation of each component to ensure proper reassembly. For example, use paint markers or labels to identify oil lines, bolts, etc.
2. Remove External Components: Dismantle external components like oil pipes, fittings, and end covers in a specific sequence. Collect small parts such as bolts and gaskets to prevent loss.
3. Disassemble Internal Components: Carefully remove internal parts including pistons, cylinder blocks, distributor plates, and swashplates. Avoid damaging component surfaces during disassembly.
Fourth, Component Inspection and Repair
1. Visual Inspection: Thoroughly examine each component for wear, scratches, cracks, deformation, etc. For example, check piston surfaces for scoring and distributor plate surfaces for wear marks.
2. Dimension Measurement: Use gauges to measure critical component dimensions and verify they fall within tolerance limits. Measurements include piston diameter, cylinder bore, etc. Replace parts if dimensions exceed tolerance.
3. Part Cleaning: Clean disassembled components with appropriate detergents to remove oil residue and contaminants. After cleaning, dry thoroughly with a clean cloth or compressed air.
4. Part Repair or Replacement: Minorly worn parts may be repaired, such as lapping the distributor plate surface or fixing slight scratches on the plunger. Severely worn or damaged components must be replaced, such as seals, pistons, bearings, etc.
Fifth, Assemble the Pump Housing
1. Apply Lubricant: Before assembly, coat all component surfaces with an appropriate amount of clean hydraulic oil to reduce friction during assembly and provide lubrication for initial pump operation.
2. Assemble according to markings: Install each component into the pump body sequentially based on previously marked and recorded positions and orientations. Pay close attention to assembly sequence and fit accuracy to ensure all parts are correctly installed.
3. Tighten bolts: Use appropriate tools to tighten bolts to specified torque values, avoiding over-tightening or under-tightening. Undercut bolts may cause leakage, while overtightening may damage components.
Kawasaki K3VI pump
Swash plate pump K5V
 French
French
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Russian
Russian
 German
German
 Spanish
Spanish
 Japanese
Japanese
 Korean
Korean
 Irish
Irish
 Greek
Greek
 Turkish
Turkish
 Italian
Italian
 Danish
Danish
 Romanian
Romanian
 Indonesian
Indonesian
 Czech
Czech
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
 Swedish
Swedish
 Polish
Polish
 Basque
Basque
 Catalan
Catalan
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Hindi
Hindi
 Lao
Lao
 Albanian
Albanian
 Amharic
Amharic
 Armenian
Armenian
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani
 Belarusian
Belarusian
 Bengali
Bengali
 Bosnian
Bosnian
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Cebuano
Cebuano
 Chichewa
Chichewa
 Corsican
Corsican
 Croatian
Croatian
 Dutch
Dutch
 Estonian
Estonian
 Filipino
Filipino
 Finnish
Finnish
 Frisian
Frisian
 Galician
Galician
 Georgian
Georgian
 Gujarati
Gujarati
 Haitian
Haitian
 Hausa
Hausa
 Hawaiian
Hawaiian
 Hebrew
Hebrew
 Hmong
Hmong
 Hungarian
Hungarian
 Icelandic
Icelandic
 Igbo
Igbo
 Javanese
Javanese
 Kannada
Kannada
 Kazakh
Kazakh
 Khmer
Khmer
 Kurdish
Kurdish
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz
 Latin
Latin
 Latvian
Latvian
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Macedoniar
Macedoniar
 Malagasy
Malagasy
 Malay
Malay
 Malayalam
Malayalam
 Maltese
Maltese
 Maori
Maori
 Marathi
Marathi
 Mongolian
Mongolian
 Burmese
Burmese
 Nepali
Nepali
 Norwegian
Norwegian
 Pashto
Pashto
 Persian
Persian
 Punjabi
Punjabi
 Serbian
Serbian
 Sesotho
Sesotho
 Sinhala
Sinhala
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovenian
Slovenian
 Somali
Somali
 Samoan
Samoan
 Scots Gaelic
Scots Gaelic
 Shona
Shona
 Sindhi
Sindhi
 Sundanese
Sundanese
 Swahili
Swahili
 Tajik
Tajik
 Tamil
Tamil
 Telugu
Telugu
 Thai
Thai
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian
 Urdu
Urdu
 Uzbek
Uzbek
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Welsh
Welsh
 Xhosa
Xhosa
 Yiddish
Yiddish
 Yoruba
Yoruba
 Zulu
Zulu







